
Involves absorption or liberation of energy.Ī reaction of a type: AB + CD ⟶ AD + CB, involves Reason - Characteristics of a chemical change are : (iv) Involves absorption or liberation of energy Which of the following is not a characteristic of a chemical change? Heat - Some chemical reactions occur only on heating.ĬuCO 3 (s) → Δ \xrightarrow brown Cu (s) + conc. Solution - In some cases, a chemical reaction occurs when substances are mixed either in molten or aqueous state. These reactions are called reversible changes. Pb(NO 3) 2 (s) + 2KI (s) ⟶ 2KNO 3 + PbI 2 (s) A few chemical reactions can be reversed the original materials can be re-created from the new materials. Mixing (close contact) - Some chemical reactions take place when two substances are mixed in their solid state. (b) Conditions necessary for a chemical change or reaction are : Only the physical qualities of the material, such as its size and shape, tend to change in a reversible alteration. One or more approaches can be used to undo this alteration. (a) A chemical reaction is a process of breaking chemical bonds of the reacting substances (reactants) and making new bonds to form new substances (products). The term 'reversible change' refers to a chemical alteration that can be undone. (b) State the conditions necessary for a chemical change or reaction. This text is adapted from Openstax, Anatomy and Physiology 2e, Section 24.1: Overview of Metabolic Reactions and Openstax, Biology 2e, Section 2.1: Atoms, Isotopes, Ions and Molecules: The Building Blocks.Chapter 2 Chemical Changes and Reactions Class 9 - Concise Chemistry Selina

When there is excess hydrogen ions in the blood, forming carbonic acid will be the reaction's major direction. A more general term for rusting and other similar processes is corrosion. A chemical property of iron is that it is capable of combining with oxygen to form iron oxide, the chemical name of rust. If we added carbonic acid to this system, some of it would convert to bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. A chemical property describes the ability of a substance to undergo a specific chemical change. However, biological reactions rarely obtain equilibrium because the concentrations of the reactants or products or both are constantly changing, often with one reaction's product a reactant for another. A chemical equation with a double-headed arrow pointing towards both the reactants and products often denotes these reversible reaction situations.įor example, in human blood, hydrogen ions (H +) bind to bicarbonate ions (HCO 3 -), forming an equilibrium state with carbonic acid (H 2CO 3). This back and forth continues until a certain relative balance between reactants and products occurs-a state called equilibrium. At this point, product and reactant designations reverse. In those cases, the material that was altered returns to its original state. In reversible reactions, reactants turn into products, but when the product's concentration goes beyond a certain threshold (characteristic of the particular reaction), some of these products convert back into reactants. Introduction Substances can change in many ways.

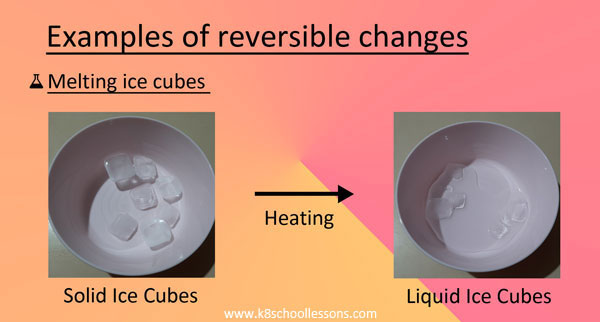
The reactions which are reversible are called reversible reactions. In theory, any chemical reaction can proceed in either direction under the right conditions. A reversible change is a change that can be undone or reversed.
#Are chemical changes reversible series#
Oxidation-reduction reactions often happen in a series so that a molecule that is reduced is subsequently oxidized, passing on not only the electron it just received but also the energy it received. These two reactions always happen together, and when an electron is passed between molecules, the donor is oxidized, and the recipient is reduced. The loss of an electron (oxidation) releases a small amount of energy both the electron and the energy are then passed to another molecule in the process of reduction or the gaining of an electron. A molecule gives up a hydrogen atom in the form of a hydrogen ion (H +) and an electron, breaking the molecule into smaller parts. The electrons in these reactions commonly come from hydrogen atoms, which consist of an electron and a proton. These reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one compound to another. An exchange reaction is a chemical reaction in which both synthesis and decomposition occur, chemical bonds are both formed and broken, and chemical energy is absorbed, stored, and released.Ī special kind of exchange reaction is the oxidation-reduction reaction, or the redox reaction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
